Ernest Scheidel
HOUSTON (Reuters) – In a milestone within the world clear power transition, Battery Metals Worldwide has grow to be the primary firm to commercially produce lithium utilizing a brand new filtration know-how, a transfer anticipated to result in cheaper, quicker energy provide. Automotive battery metallic.
At a facility in rural Utah managed by privately held US Magnesium, IBAT this week started producing business portions of lithium utilizing its direct lithium extraction (DLE) know-how at a charge of practically 5,000 tons per 12 months.
This breakthrough has not been beforehand reported.
The corporate has developed a transportable DLE plant and has basically crushed out Customary Lithium, SLB, Rio Tinto (NYSE:), Eramet and others to be the primary to get there. Trade traders, analysts and prospects have been ready for years for commercial-quality output.
With DLE now confirmed on a business scale, analysts say it’s anticipated to develop right into a $10 billion-a-year business inside a decade by altering the pace and effectivity of lithium manufacturing for electrical car producers and different corporations. Fracking is like some other know-how.
IBAT’s strategy is predicated partly on know-how developed by IBAT Chairman John Burba at The Dow Chemical Firm within the Nineteen Eighties. “That is all about rising the worldwide provide of lithium,” Burba mentioned. “We really feel the business is at a crucial second.”
The U.S. Geological Survey estimates that saltwater deposits in Europe, Asia, North America and different areas include about 70% of the world’s ultralight metallic reserves.
Traditionally, lithium has been produced by means of evaporation ponds, that are used to extract metals from brine, or open-pit mines, that are used to extract metals from laborious rock sediments. The big water use and bodily footprint of those strategies, in addition to their prolonged growth and manufacturing instances, prompted a seek for a 3rd choice.
Whereas DLE applied sciences fluctuate, they’re corresponding to widespread residence water softeners and are designed to extract about 90% or extra of the lithium from salt water, whereas utilizing a pond can solely extract about 50%.
Arcadium Lithium and some different corporations have used DLE processes along with ponds, however no DLE know-how has beforehand been produced commercially with out them, sparking a race to increase manufacturing to many areas of the world the place rainfall is occasional. Making evaporation ponds impractical.
Analysts say the chemical composition of many saltwater sediments varies, which means any single DLE know-how, together with IBAT, is unlikely to grow to be a worldwide commonplace. For instance, many mineral deposits in China include excessive concentrations of magnesium, whereas deposits in Bolivia (one of many largest on the planet) additionally include excessive ranges of potassium.
Lithium has repeatedly confirmed troublesome to separate from these and different metals which can be typically combined in brine. This has puzzled many scientists who’ve been engaged on DLE know-how for a few years. Lithium can also be technically a salt and is corrosive.
IBAT’s breakthrough coincides with a greater than 80% drop in lithium costs over the previous 12 months, resulting in layoffs on the business chief Albemarle (NYSE: ), DLE upstart Lake Assets, and others. Nonetheless, IBAT plans to construct extra crops and promote them around the globe.
Technique
IBAT mentioned the corporate’s success in attaining commercial-scale manufacturing is partly as a result of comparatively small dimension of its factories.
Though opponents have been making an attempt to commercialize DLE for greater than a decade, their plans have concerned everlasting services of 20,000 tons per 12 months or extra, typically in distant areas the place labor and provides are troublesome to supply.
Houston-based IBAT designed and constructed a 450-foot-long (137-meter) transportable plant in 13 sections in Louisiana that was moved to the US Magnesium plant, which pumps brine from the Nice Salt Lake.
Extra crops may be added and stacked like Lego blocks to extend manufacturing in increments of 5,000 tons per 12 months. The corporate mentioned it can take 18 months to construct and begin manufacturing on the IBAT manufacturing unit.
Every plant is lower than three acres (1.2 hectares) in dimension and is designed to be relocated to a brand new mine web site for future reuse, saving on development prices. IBAT prices $50 million to $60 million per plant, relying on a number of elements.
Paris-based Eramet is spending practically $900 million to develop its personal DLE undertaking, which is scheduled to come back on-line in Argentina this 12 months after greater than a decade of growth.
Ron Thayer, president of US Magnesium, mentioned he selected the IBAT course of due to its portability and the kind of adsorbent materials it makes use of to filter lithium from brine (developed by Burba).
He added that US Magnesium, which has begun promoting lithium produced utilizing IBAT know-how and paying royalties to IBAT, thought-about quite a lot of rival processes earlier than deciding on IBAT, together with one from Breakthrough Power Ventures-backed Lilac Options. Craftsmanship.
“I feel (IBAT) is a business lithium producer,” Thayer mentioned
Exxon Mobil In response to Reuters, an organization creating a lithium undertaking in Arkansas has thought-about utilizing IBAT’s know-how.
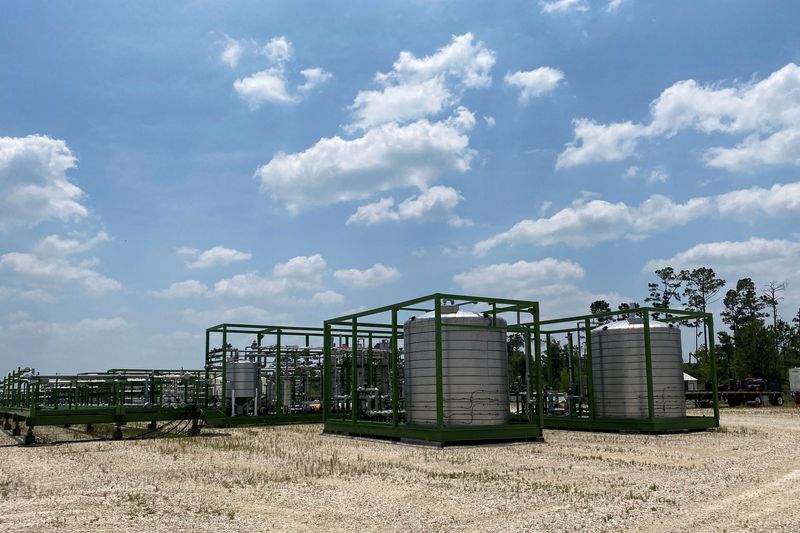

The IBAT plant goals to recycle greater than 98% of the water it makes use of. Burba has repeatedly pointed to the lithium business’s excessive water utilization as a structural impediment to the commercialization of DLE.
Recyclability is very crucial in Utah, the place state officers final 12 months tightened laws on Nice Salt Lake water extraction, forcing Compass Minerals to desert its lithium plans.