Mosquitoes cringe on the sight of human arms. That is proper: Vampires depend on thermal infrared gentle to seek out simply the precise chunk spot to make you’re feeling itchy and doubtlessly sick.
Underneath analysis publish This week in Nature, a bunch of biologists describe a mosquito’s infrared detector Aedes aegypti and its related morphological and biochemical constructions. “This contains carbon dioxide2 From the breath, scent, and sight we exhale, [convection] warmth from our pores and skin and moisture from our our bodies,” Avinash Chandel, a biologist at UC Santa Barbara and co-lead writer of the research, stated in a press launch. “Nevertheless, these clues have limitations.”
Along with itchy welts, mosquito bites can transmit ailments akin to dengue fever, yellow fever, and Zika virus. A latest group of researchers needed to discover precisely what capabilities animals use when looking for hosts for his or her blood-sucking mischief.
Mosquitoes do not have superb eyesight, in order that they depend on a number of senses to seek out animals to chunk. Their senses additionally shield them from hazard. one 2022 Paper Mosquitoes reply to visible and mechanical indicators that point out they’re dealing with a risk whereas feeding (i.e., an open hand able to flap), present in Scientific Experiences.
Mosquitoes can detect warmth rising from human pores and skin inside about 4 inches (10 centimeters) of it. As soon as bugs land on our pores and skin, they’ll instantly sense the pores and skin’s temperature. However in line with new analysis, animals additionally detect thermal infrared gentle.
The researchers measured how feminine mosquitoes discovered hosts in two areas that had been uncovered to human odor and the identical focus of carbon dioxide we exhale. However one of many areas was uncovered to thermal infrared gentle from a pores and skin temperature supply, which the researchers discovered doubled the mosquito’s host-finding exercise. When an infrared supply is activated, the mosquito’s warmth sensitivity seems to leap to about 2.5 ft (70 centimeters).
“No single clue stimulates a seek for a number,” Craig Montel, a biologist on the College of California, Santa Barbara and senior writer of the research, stated in a press launch. “This solely happens within the context of different clues, akin to elevated carbon dioxide ranges.2 In addition to human odor, infrared rays had an influence.
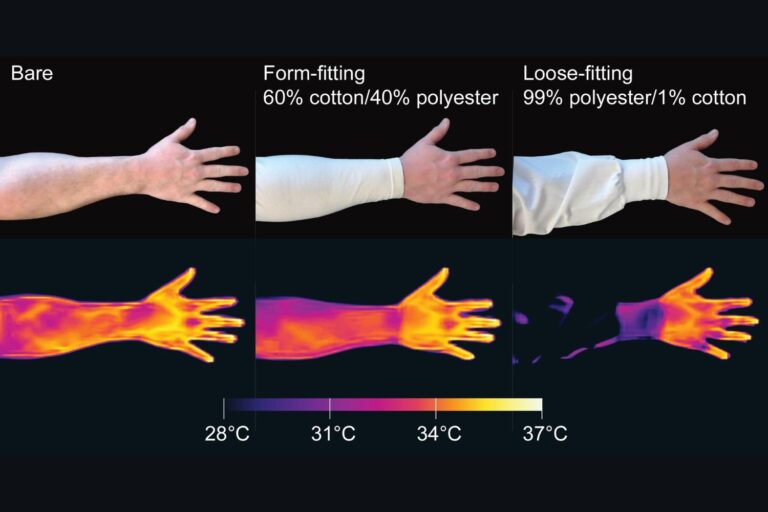
The group believes that free clothes could also be an particularly good protection towards mosquitoes as a result of it leaves area between the pores and skin and clothes for thermal infrared rays to dissipate, making it tougher for bugs to discover a host.
In recent times, Aedes aegyptiIts footprint has expanded from its historic vary within the tropics and subtropics. The species’ vary now extends into California and different elements of the US. Understanding extra about the way in which mosquitoes discover us will assist researchers discover methods to discourage the pests, thereby lowering the unfold of mosquito-borne ailments.